 San Antonio Area Hams
San Antonio Area Hams 
![]()
 QRZ.com provides a forum whereby you can register for free (using your ham call sign, plus a password) and be able to participate in discussion groups on various topics, or post questions to ask other hams. QRZ.com also has links to a multitude of information, ranging from software, to radio mods, to vendor links. QRZ.com has on-line testing for the various classes of ham licenses as a free service as well.
QRZ.com provides a forum whereby you can register for free (using your ham call sign, plus a password) and be able to participate in discussion groups on various topics, or post questions to ask other hams. QRZ.com also has links to a multitude of information, ranging from software, to radio mods, to vendor links. QRZ.com has on-line testing for the various classes of ham licenses as a free service as well.
Most of the hams who have been around for awhile, know about the free service offered by QRZ.com were you can perform a callsign database search by callsign or name. Or for that matter, by city, county, state, well, you get the idea. But if the number of valid searches is greater than 500, they only display the first 500 records found.
What some hams apparently aren't aware of however, is that you can log in on QRZ.com and update or provide your own Biography and Photograph. See this web link for an example of how the webmaster for SanAntonioHams.org has updated his. Each ham can control unlimited numbers of other call signs, but if they catch you abusing this, such as purposely altering another ham's records improperly, you will be banned from QRZ.com. Once someone registers as control of another call sign, nobody else may alter it. An example might be if you were trustee for a club call and needed to keep it updated. Another would be if a friend become a silent key (deceased ham) and their bio needed changed to provide details. All photos are examined manually prior to posting, and photos in bad taste will never appear. Read their guidelines before posting. You can also provide your email address for contact info, and they create an image with your address in it, not a clickable email link. This is to reduce harvesting of email addresses by SPAMMERS.
Ham Radio Terms, Lingo, Slang, Abreviations Let us help you get rid of your confusion.
|
![]()
eham.net offers much of the same services that QRZ.com does, such as a forum for discussing, on-line practice tests, radio mods, software downloads, etc. but they also have classified ads sections in addition. Once again, you have to register (free service) as a member of Eham.net , and then fill out your profile and jump on in. We do recommend spending some time reading other ham's postings before posting your own opinions or questions because you might find that someone has already answered that question for you. Got questions about a particular radio? Not a problem. Eham.net has a section that allows hams to post reviews of their favorite, or most hated as the case may be, radio to share their opinion with other readers. Got something to sell or want to buy? Eham.net had their classified ads out for longer then eBay, we think. And there is no charge for using that service because you are buying / selling direct with the other party. Be aware, there is not a third party guarantee like you find on eBay to protect you against being taken by an unscrupulous seller, but Eham.net will try to filter out those types of persons when reported.
![]()
QSL.NET was started in the Winter of 1996 by K3TKJ as an experiment in managing a live Internet network and learning the Linux Operating System. The System has grown by word of mouth to be largest site devoted totally to Amateur Radio on the Internet. QSL.NET is a hobby site not a business, he do this because it allows him to give back to ham radio some of what it has given him.
QSL.NET is dedicated to the sole purpose of furthering the abilities and interest of the Amateur Radio Community. If you are a licensed Amateur Radio Operator you are invited to reserve your free space on QSL.NET NOW. Sign Up and you will receive free E-Mail, with forwarding to your existing service, along with free server space to either move your homepage to this server, mirror your existing one, or lose all those excuses and finally START one. Now to the hard part, what do you have to do?? That is really the easy part, just move to the left side of the screen and "click" the part that says Sign Up for a FREE Homepage or E-mail Account! It is that easy, go ahead, do it NOW!
Recently QSL.NET went over 800,000 users, it sends and receives over 2 million e-mails daily....and has online over 70,000 individual and club web pages. Not links...the pages live here. Now 10 years old, QSL.NET , QTH.NET and SWL.NET are the largest collection points of ham radio knowledge to be found anywhere.
The QSL.NET system consists of 21 servers offering FREE services....all you need is to be a ham. 73, Al Waller,
K3TKJ, QSL.NET , Inc.
![]()
 Thinking about QSL cards, and the high cost of sending SASE envelopes to request copies of the other ham's QSL? How about getting an electronic card that you can send / receive free of charge? Well, there is a fairly new web site out there call eQSL.cc which offers exactly that service. Free to sign up for basic service level, but you can pay $ to upgrade to higher levels of membership where you can have fancier QSL cards if you have an ego that needs polished.
Thinking about QSL cards, and the high cost of sending SASE envelopes to request copies of the other ham's QSL? How about getting an electronic card that you can send / receive free of charge? Well, there is a fairly new web site out there call eQSL.cc which offers exactly that service. Free to sign up for basic service level, but you can pay $ to upgrade to higher levels of membership where you can have fancier QSL cards if you have an ego that needs polished.
eQSL.cc is the first and only global electronic QSL card exchange for amateur radio operators and SWLs. It is designed to be the fastest, easiest, and cheapest way to exchange QSO confirmations, eliminating the cost and time that regular QSL cards have required for the past half century.
The company is registered in the State of Texas and owned by David L. Morris, N5UP. Dave has over 25 years of experience architecting computer hardware and software systems and has been involved in other pioneering software projects involving amateur radio and artificial intelligence. He experimented and developed the eQSL.cc concept over a period of several years, designed the system, wrote all the software, developed the SQL database, designed the graphics, and currently handles much of the technical support.
 Claims to be the world's largest radio communications reference website, with complete conventional frequency assignments, trunked radio system information, frequencies, and talkgroups, FCC License assignments and maps, 10-Code Lists, agency maps, files, downloads, links, and detailed agency information for most public safety, military, and local government activities. All of this can be found in the Radio Reference Database.
The Radio Reference Forums provide the largest most popular place to come and talk about radio communications monitoring.
Claims to be the world's largest radio communications reference website, with complete conventional frequency assignments, trunked radio system information, frequencies, and talkgroups, FCC License assignments and maps, 10-Code Lists, agency maps, files, downloads, links, and detailed agency information for most public safety, military, and local government activities. All of this can be found in the Radio Reference Database.
The Radio Reference Forums provide the largest most popular place to come and talk about radio communications monitoring.
 An independent source of Amateur Radio news from around the world available weekly in both text and MP3 formats. Many of the ham clubs around the world re-broadcast this recording during their weekly radio club net. Locally in San Antonio, the AARO Ham Club broadcasts this on their Monday night net at 8:30pm, prior to their check-in net at 9pm. You can click on either of the links below to download either a text or audio version of the news.
An independent source of Amateur Radio news from around the world available weekly in both text and MP3 formats. Many of the ham clubs around the world re-broadcast this recording during their weekly radio club net. Locally in San Antonio, the AARO Ham Club broadcasts this on their Monday night net at 8:30pm, prior to their check-in net at 9pm. You can click on either of the links below to download either a text or audio version of the news.
 This amateur radio web site explains how to use the AGWPE utility program to send and receive packet (a digital data mode) using the sound card of your PC instead of a traditional TNC (Terminal Node Controller), a radio modem. The site offers: instructions for configuring AGWPE, Windows, and some compatible packet programs advice about building or buying a sound card-to-radio interface troubleshooting advice.
This amateur radio web site explains how to use the AGWPE utility program to send and receive packet (a digital data mode) using the sound card of your PC instead of a traditional TNC (Terminal Node Controller), a radio modem. The site offers: instructions for configuring AGWPE, Windows, and some compatible packet programs advice about building or buying a sound card-to-radio interface troubleshooting advice.
The key to sound card packet is a free program called AGWPE. AGWPE was written by George Rossopoulos, SV2AGW, and is an acronym for " SV2AGW's Packet Engine". It was originally created as a TNC management utility and has many super features of value to TNC users, however, this web site deals primarily with AGWPE's ability to encode and decode packet tones using your computer's sound card. AGWPE is the only program that can do this, other than MixW and Flexnet32. AGWPE is particularly valuable since it can act as a "host" program for several good packet programs that do not have sound card packet capabilities of their own. In June 2003, George SV2AGW released a new program, Packet Engine Pro, based on the original, freeware AGWPE program, but this version does cost $49. This module is also highly recommended to purchase if you plan on running the new Winlink2000 software in addition to Packet.
Why use a sound card instead of a real TNC? First of all, it can be much cheaper. You only need a sound card interface, which is a set of cables to connect your sound card to your radio. Interfaces can be made for a few dollars or purchased for as little as $30-40 US, while the cheapest external TNC costs at least 100 US. And if you use the stereo qualities of the sound card to simulate two TNCs, so you could be saving the cost of two TNCs! Other good reasons are that an interface is lighter and less bulky than a TNC and an interface usually requires no external power; a TNC will need some power source.
Another reason is that according to the program author, George SV2AGW, the AGWPE soundcard modem gives better results than a TNC . George says the 300 baud HF modem is so sensitive that it decodes packets you cannot hear; the 1200 baud modem can decode packets even with S3 or less signal strength; and the 9600 baud modem is better than the original G3RUH. To be fair, other users claim they get better results with a TNC; that TNCs are easier to setup; and that TNCs usually have built-in watch-dog timers to prevent continuous transmitting in the event of an error.
Limitations: To be fair, other users claim they get better results with a TNC; that TNCs are easier to setup; and that TNCs usually have built-in watch-dog timers to prevent continuous transmitting in the event of an error. Note that most packet programs will not work with AGWPE. Only compatible programs that have been specifically written to take advantage of AGWPE's host services will work, but there are several good ones.
Hardware Requirements: AGWPE will run in Windows 95, 98, ME, XP, 2000 and Vista. It will not run in plain old DOS or Windows 3.1. Some users have been able to run it on NT 4.0. The sound card features of AGWPE should work with most 16 or 32-bit sound cards (and integrated main board sound chips), although it will not run on all cards (see compatible sound cards). You should also have the most up-to-date drivers for your sound card.
![]()
 I recently installed a new transceiver in my truck. On the first day of using the new radio I got reports that I was transmitting very noticeable alternator whine. I could also hear it on receive and when the radio was quiet. I checked the diodes in the alternator, verified I had good grounds, and I even ran the truck with the alternator removed to be sure that the whine was indeed from the alternator. I tried an off the shelf filter from Advance Auto. It did very little so I decided to build a filter. The first filter I built worked VERY well. The problem is that not everyone has the tools required to build that filter so I decided to figure out a filter design that could be built in less than an hour by anyone with basic tools, have a cost under $20, and handle a current draw of at least 20 Amps.
I recently installed a new transceiver in my truck. On the first day of using the new radio I got reports that I was transmitting very noticeable alternator whine. I could also hear it on receive and when the radio was quiet. I checked the diodes in the alternator, verified I had good grounds, and I even ran the truck with the alternator removed to be sure that the whine was indeed from the alternator. I tried an off the shelf filter from Advance Auto. It did very little so I decided to build a filter. The first filter I built worked VERY well. The problem is that not everyone has the tools required to build that filter so I decided to figure out a filter design that could be built in less than an hour by anyone with basic tools, have a cost under $20, and handle a current draw of at least 20 Amps.
![]()
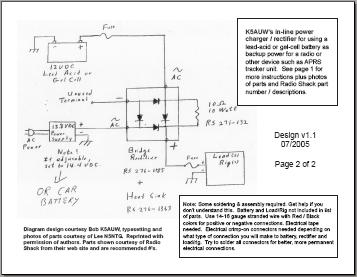 At one of the AARO club meetings, Bob K5AUW passed out a hand written diagram showing how to build your own charger circuit. This allows you to connect 12 volt power to this circuit, that will pass it along to your radio or other device, plus (and here's the trick) simultaneously charge the connected backup battery. If the external 12 volt power (DC) fails, the circuit allows the radio to draw power from the attached battery.
At one of the AARO club meetings, Bob K5AUW passed out a hand written diagram showing how to build your own charger circuit. This allows you to connect 12 volt power to this circuit, that will pass it along to your radio or other device, plus (and here's the trick) simultaneously charge the connected backup battery. If the external 12 volt power (DC) fails, the circuit allows the radio to draw power from the attached battery.
![]()
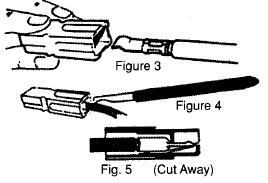 The local ARES group recently asked all of their members to become "Anderson Powerpole Compliant" in their vehicles. This was so that they would be able to install and use city provided emergency radios if deployed with such, and to encourage the use of these more reliable connectors.
The local ARES group recently asked all of their members to become "Anderson Powerpole Compliant" in their vehicles. This was so that they would be able to install and use city provided emergency radios if deployed with such, and to encourage the use of these more reliable connectors.
Either the 15-ampere, 30-ampere or 45-ampere sizes may be used, and both sizes mate with each other. The plastic parts are the same for both sizes. In fact, there is even a 75-ampere size available for a much higher cost per pair of connectors, that will handle 6, 8 or 10-12 gauge wire. Usually the 30-ampere size is used for most installations, but if you need to feed a group of radios from one wire, we recommend use of the 45-ampere or 75-ampere rated connections with the higher gauge wire. (Note: the cost of 75-ampere connectors is triple the expense of 45-ampere connectors. Most common size is the 30-ampere connectors.)

About Us | Privacy Policy | Contact Us | ©2003-2016 Lee W. Besing, N5NTG - San Antonio Hams